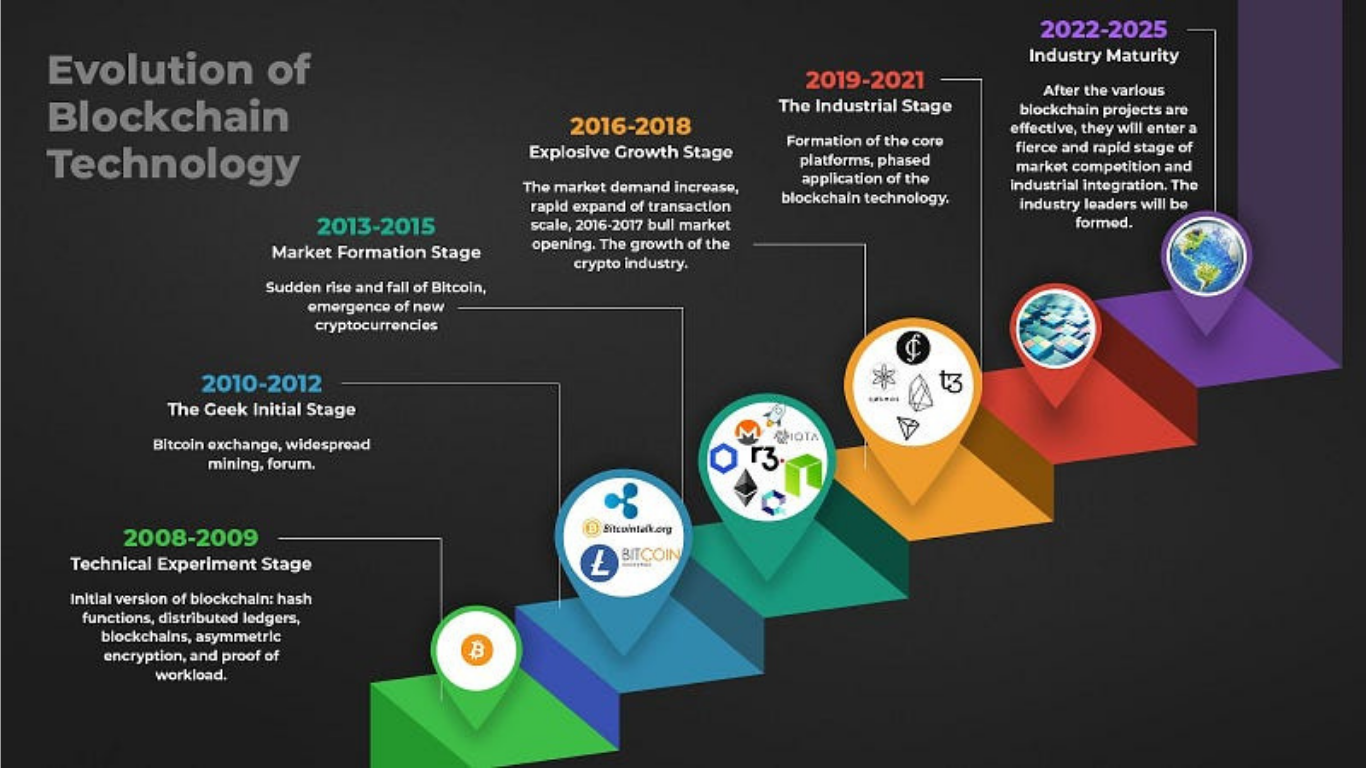
Introduction
Blockchain technology has undergone a remarkable transformation since Bitcoin’s inception in 2008. What began as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system has evolved into a foundational technology powering decentralized finance (DeFi), smart contracts, NFTs, and enterprise solutions.
This article explores:
✔ Key phases of blockchain evolution (2008–present).
✔ Major technological breakthroughs.
✔ How different industries adopted blockchain.
✔ Future trends in decentralized systems.
By the end, you’ll understand how blockchain grew from a niche experiment to a global disruptor.
1. Phase 1: The Birth of Blockchain (2008–2013)
A. Bitcoin & Proof-of-Work (2009)
- Satoshi Nakamoto’s whitepaper introduced:
- Decentralized ledger (blockchain).
- Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus.
- Fixed supply (21M BTC).
- Use Case: Digital gold & censorship-resistant payments.
B. Early Altcoins (2011–2013)
- Litecoin (2011): Faster blocks (2.5 min vs. Bitcoin’s 10 min).
- Namecoin (2011): First non-financial blockchain use (decentralized DNS).
- Ripple (2012): Enterprise-focused payment network.
Key Innovation: Proved blockchain could be modified for different needs.
2. Phase 2: Smart Contracts & Ethereum (2014–2017)
A. Ethereum’s Launch (2015)
- Vitalik Buterin proposed a Turing-complete blockchain.
- Introduced smart contracts (self-executing code).
- ERC-20 standard enabled tokenization (ICOs boom in 2017).
B. The ICO Craze (2017)
- Startups raised $20B+ via token sales.
- Many scams, but also legitimate projects (EOS, Tezos).
Impact: Showed blockchain’s potential beyond payments.
3. Phase 3: Scalability & Enterprise Adoption (2018–2020)
A. Scaling Solutions Emerge
- Layer 2s: Lightning Network (Bitcoin), Plasma (Ethereum).
- Alternative Consensus: Proof-of-Stake (PoS), DPoS (EOS).
B. Enterprise Blockchain
- Hyperledger (IBM): Permissioned blockchains for businesses.
- CBDC Development: China’s digital yuan, FedNow experiments.
Shift: From “crypto anarchy” to institutional acceptance.
4. Phase 4: DeFi, NFTs & Mainstream Breakthrough (2021–2023)
A. DeFi Summer (2020–2021)
- Permissionless lending/borrowing (Aave, Compound).
- DEXs (Uniswap) overtook centralized exchanges.
- TVL peaked at $180B (Nov 2021).
B. NFT Boom
- CryptoPunks, Bored Apes redefined digital ownership.
- Art, gaming, IP licensing embraced NFTs.
C. Ethereum’s Merge (2022)
- Switched from PoW to PoS, cutting energy use by 99.95%.
Trend: Blockchain became multifunctional (finance, art, identity).
5. Phase 5: The Future (2024 & Beyond)
A. Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs)
- ZK-Rollups (zkSync, StarkNet) enable private, scalable transactions.
B. AI + Blockchain Fusion
- Decentralized AI training (Bittensor).
- NFT-based AI ownership.
C. Regulatory Clarity
- MiCA (EU), US crypto laws shaping industry standards.
Prediction: Mass adoption via seamless, regulated, user-friendly apps.
6. Conclusion: From Cypherpunk Dream to Global Infrastructure
Blockchain’s evolution mirrors the internet’s early days—disruptive, iterative, and unstoppable.
Key Takeaways:
✅ 2009–2013: Bitcoin proved decentralized money works.
✅ 2014–2017: Ethereum added programmability.
✅ 2018–2020: Enterprises & governments took notice.
✅ 2021–2023: DeFi & NFTs went mainstream.
✅ 2024+: Scalability, privacy, AI integration will dominate.
Final Thought:
“If blockchain is still in its ‘dial-up’ phase, what will broadband look like?”
FAQs
Q: What was blockchain’s biggest leap forward?
A: Ethereum’s smart contracts (2015), enabling apps beyond payments.
Q: Will Bitcoin ever adopt smart contracts?
A: Limited functionality via RGB, Stacks, but Ethereum remains dominant.
Q: Is blockchain only for finance?
A: No—healthcare, voting, supply chains are adopting it.